Is there a functional relationship between hydration and memory in children and adolescents? A meta-analysis.
Main Article Content
Abstract
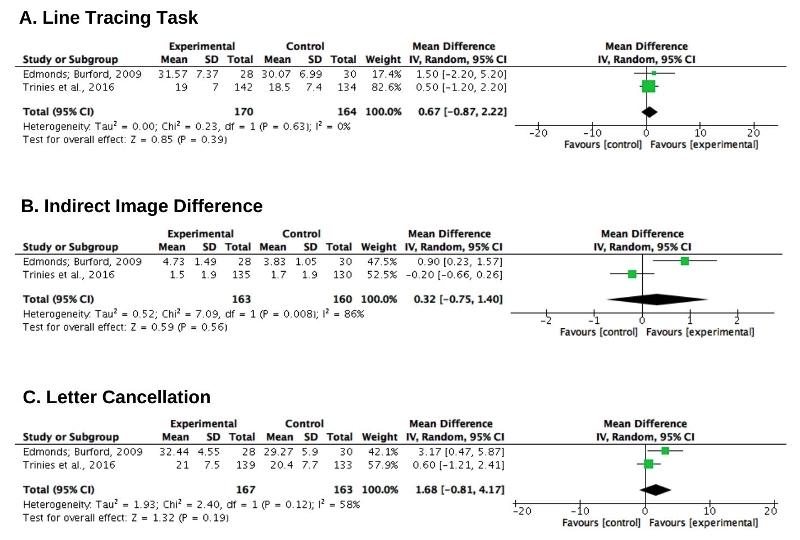
Objective: Hydration can favor cognitive functions during childhood and adolescence, helping with daily and school activities. This study aimed to identify possible interactions between hydration and memory in children and adolescents. Methods: This is a systematic review with meta-analysis. The bibliographic search was conducted in the MEDLINE/PubMed, SciELO, LILACS, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases, through a combination of the descriptors: “hydration” AND “memory”; “hydration” AND “memory” AND “child”; “hydration” AND “memory” AND “children”; “organism hydration status” AND “memory”; “organism hydration status” AND “memory” AND “child”. Results: The search resulted in 816 articles, of which ten were selected for qualitative synthesis and two for the meta-analysis. The results indicated that hydration could not enhance working, visual and visuomotor memories, or visual attention (Line Tracing Task, MD 0.67, 95% CI -0.87 to 2.22; Indirect Image Difference, MD 0.32, 95% CI -0.75 to 1.40; Letter Cancellation, MD 1.68, 95% CI -0.81 to 4.17). Conclusion: From the obtained results, hydration per se does not reinforce working, visual and visuomotor memories, or visual attention. However, there are still gaps regarding other types of memory and cognitive, motor, nutritional and environmental integration.
Article Details
Authors maintain copyright and grant the HSJ the right to first publication. From 2024, the publications wiil be licensed under Attribution 4.0 International 
 , allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
, allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are authorized to assume additional contracts separately for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in this journal (e.g., publishing in an institutional repository or as a book chapter), with acknowledgment of authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are encouraged to publish and distribute their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their personal page) at any point after the editorial process.
Also, the AUTHOR is informed and consents that the HSJ can incorporate his article into existing or future scientific databases and indexers, under the conditions defined by the latter at all times, which will involve, at least, the possibility that the holders of these databases can perform the following actions on the article.
References
Krecar IM, Kolega M, Kunac SF. The effects of drinking water on attention. Procedia - Soc Behav Sci. 2014;159:577-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.12.428
Riebl SK, Davy BM. The hydration equation: update on water balance and cognitive performance. ACSMs Health Fit J. 2013;17(6):21-8. https://doi.org/10.1249/FIT.0b013e3182a9570f
Armstrong LE. Hydration assessment techniques the importance of hydration assessment. Nutr Rev. 2005;63(supl 1):S40-54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2005.tb00153.x
Schmit C, Hausswirth C, Le Meur Y, Duffield R. Cognitive functioning and heat strain: performance responses and protective strategies. Sport Med. 2017;47(7):1289-302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-016-0657-z
Benton D. Dehydration influences mood and cognition: A plausible hypothesis? Nutrients. 2011;3(5):555-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu3050555
Fadda R, Rapinett G, Grathwohl D, Parisi M, Fanari R, Calò CM, et al. Effects of drinking supplementary water at school on cognitive performance in children. Appetite. 2012;59(3):730-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2012.07.005 PMID:22841529
Edmonds CJ, Burford D. Should children drink more water? The effects of drinking water on cognition in children. Appetite. 2009;52(3):776-9 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2009.02.010
Khan NA, Raine LB, Drollette ES, Scudder MR, Cohen NJ, Kramer AF, et al. The relationship between total water intake and cognitive control among prepubertal children. Ann Nutr Metab. 2015;66(Supl 3):38-41. https://doi.org/10.1159/000381245 PMID:26088046
Perry CS 3rd, Rapinett G, Glaser NS, Ghetti S. Hydration status moderates the effects of drinking water on children's cognitive performance. Appetite. 2015;95:520-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2015.08.006 PMID:26271221
Trinies V, Chard AN, Mateo T, Freeman MC. Effects of water provision and hydration on cognitive function among primary-school pupils in Zambia: A Randomized Trial. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150071. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150071 PMID:26950696 PMCID:PMC4780815
Mourão CA, Faria NC. Memória. Psicol Reflex Crit. 2015;28(4):780-788. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-7153.201528416
Mayford M, Siegelbaum SA, Kandel ER. Synapses and memory storage. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4(6):a005751. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a005751 PMID: 22496389 PMCID:PMC3367555
von Hameln. Memórias. Arq Maaravi. 2013;7(12):203-5. https://doi.org/10.17851/1982-3053.7.12.203-205
Cantarino JMF, Pereira DA. Memória: da filosofia à neurociência. Univ Ciênc Saúde. 2004;2(2):164-99. https://doi.org/10.5102/ucs.v2i2.531
Milner B, Squire LR, Kandel ER. Cognitive neuroscience and the study of memory. Neuron. 1998;20(3):445-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80987-3 PMID:9539121
Gerbasi GLBS, da Costa PJ. As transformações da memória: Articulações entre Sigmund Freud e Eric Kandel. Av Psicol Latinoam. 2015;33(1):77-89. https://doi.org/10.12804/apl33.01.2015.06
Bailey CH, Kandel ER, Harris KM. Structural components of synaptic plasticity and memory consolidation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(7):a021758. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a021758 PMID:26134321 PMCID:PMC4484970
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, Thomas J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10:ED000142. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.ed000142 PMID:31643080
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;350:g7647. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647. Erratum in: BMJ. 2016;354:i4086. PMID:25555855
Morgan RL, Whaley P, Thayer KA, Schünemann HJ. Identifying the PECO: A framework for formulating good questions to explore the association of environmental and other exposures with health outcomes. Environ Int. 2018;121(Pt 1):1027-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.07.015 PMID:30166065 PMCID:PMC6908441
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016;355:i4919. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i4919 PMID:27733354 PMCID:PMC5062054
McGuinness LA, Higgins JPT. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res Synth Methods. 2021;12(1):55-61. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1411 PMID:32336025
Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. Version 5.4. The Cochrane Collaboration (2020).
Benton D, Burgess N. The effect of the consumption of water on the memory and attention of children. Appetite. 2009;53(1):143-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2009.05.006 PMID:19445987
Chard AN, Trinies V, Edmonds CJ, Sogore A, Freeman MC. The impact of water consumption on hydration and cognition among schoolchildren: Methods and results from a crossover trial in rural Mali. PLoS One. 2019;14(1):e0210568. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210568 PMID:30653554 PMCID:PMC6336322
Khan NA, Westfall DR, Jones AR, Sinn MA, Bottin JH, Perrier ET, Hillman CH. A 4-d water intake intervention increases hydration and cognitive flexibility among preadolescent children. J Nutr. 2019;149(12):2255-64. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxz206 PMID:31504690
Edmonds CJ, Harte N, Gardner M. How does drinking water affect attention and memory? The effect of mouth rinsing and mouth drying on children's performance. Physiol Behav. 2018;194:233-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.06.004 PMID:29885324
Drozdowska A, Falkenstein M, Jendrusch G, Platen P, Luecke T, Kersting M, et al. Water consumption during a school day and children's short-term cognitive performance: The CogniDROP randomized intervention trial. Nutrients. 2020;12(5):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051297 PMID:32370147 PMCID:PMC7282257
Edmonds CJ, Crosbie L, Fatima F, Hussain M, Jacob N, Gardner M. Dose-response effects of water supplementation on cognitive performance and mood in children and adults. Appetite. 2017;108:464-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2016.11.011 PMID:27825957
Jéquier E, Constant F. Water as an essential nutrient: the physiological basis of hydration. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010;64(2):115-23. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.111 PMID:19724292
Taylor PJ, van Rosendal SP, Coombes JS, Gordon RD, Stowasser M. Simultaneous measurement of aldosterone and cortisol by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: application to dehydration-rehydration studies. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010;878(15-16):1195-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.03.033 PMID:20378424
Starkman MN, Giordani B, Gebarski SS, Berent S, Schork MA, Schteingart DE. Decrease in cortisol reverses human hippocampal atrophy following treatment of Cushing's disease. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;46(12):1595-602. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3223(99)00203-6 PMID:10624540
Bar-David Y, Urkin J, Landau D, Bar-David Z, Pilpel D. Voluntary dehydration among elementary school children residing in a hot arid environment. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2009;22(5):455-60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-277X.2009.00960.x PMID:19486262
Bar-David Y, Urkin J, Kozminsky E. The effect of voluntary dehydration on cognitive functions of elementary school children. Acta Paediatr. 2005;94(11):1667-73. https://doi.org/10.1080/08035250500254670 PMID:16303708
Drewnowski A, Rehm CD, Constant F. Water and beverage consumption among children age 4-13y in the United States: analyses of 2005-2010 NHANES data. Nutr J. 2013 Jun;12:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-12-85 PMID:23782914 PMCID:PMC3698018
Molloy CJ, Gandy J, Cunningham C, Slattery G. An exploration of factors that influence the regular consumption of water by Irish primary school children. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2008;21(5):512-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-277X.2008.00880.x PMID:18833589
World Health Organization.United Nations Children’s Fund. Drinking water, sanitation and hygiene in schools: global baseline report 2018. New York: UNICEF and WHO; 2018 [cited 2021 Jun 17]. Avaiable from: https://uni.cf/3gyKMAv
Häussinger D, Roth E, Lang F, Gerok W. Cellular hydration state: an important determinant of protein catabolism in health and disease. Lancet. 1993;341(8856):1330-2. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(93)90828-5 PMID:8098459
Deng ID, Chung L, Talwar N, Tam F, Churchill NW, Schweizer TA, Graham SJ. Functional MRI of letter cancellation task performance in older adults. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019;13:97. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2019.00097 PMID:31057377 PMCID:PMC6477506
Szinnai G, Schachinger H, Arnaud MJ, Linder L, Keller U. Effect of water deprivation on cognitive-motor performance in healthy men and women. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;289(1):R275-80. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00501.2004 PMID:15845879
Wong SH, Sun FH. Effect of beverage flavor on body hydration in Hong Kong Chinese children exercising in a hot environment. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2014;26(2):177-86. https://doi.org/10.1123/pes.2013-0080 PMID:24893377
Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for water, potassium, sodium, chloride and sulfate [Book]. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2005. https://doi.org/10.17226/10925