COVID-19 related to sarcopenia: Current perspectives on etiology, clinical implications, and nutritional rehabilitation
Main Article Content
Abstract
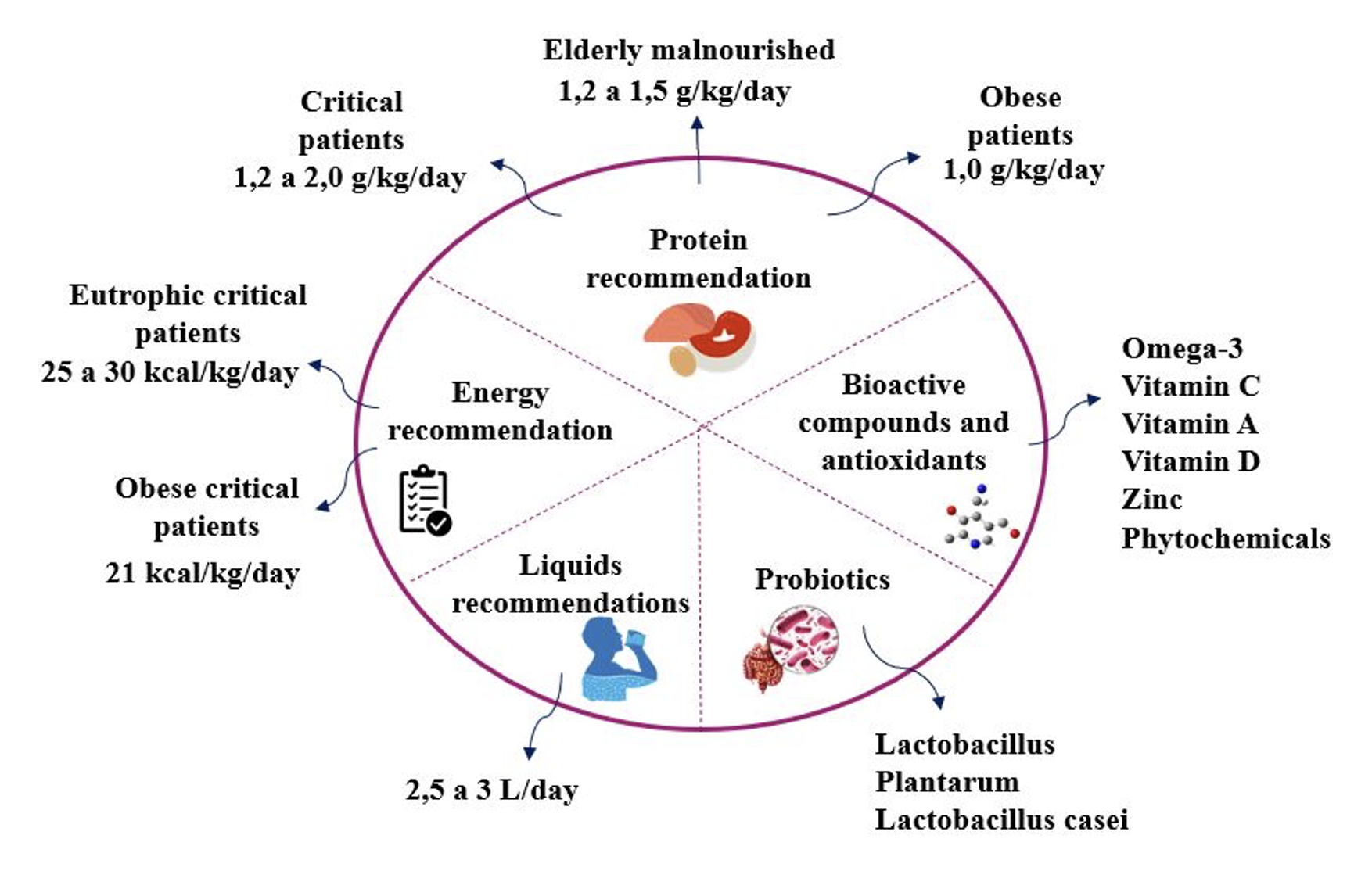
Sarcopenia is a progressive skeletal muscle disorder characterized by reduced strength and quality. Pathophysiological mechanisms, clinical aspects, and nutritional points were related to sarcopenia in COVID-19 found in skeletal muscle during and after the disease course, which corroborated the development of adverse events. Declining physical activity, insufficient protein intake, and worsened proinflammatory response have been shown to have negative consequences on muscle protein synthesis, potentiating the risk of acute sarcopenia. Obesity sarcopenia has also been shown to worsen the prognosis of patients with SARS-CoV-2. Nutritional rehabilitation is used to prevent or minimize the development of acute sarcopenia. Dietary recommendations include increased energy supply and protein intake of 1.2 to 2.0 g/kg of body weight. Evidence suggests that aging with sedentary behaviors, pathophysiological changes, and inflammation alter body composition. In addition, nutritional deficiencies are predictors and aggravators of acute sarcopenia in COVID-19.
Article Details
Authors maintain copyright and grant the HSJ the right to first publication. From 2024, the publications wiil be licensed under Attribution 4.0 International 
 , allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
, allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are authorized to assume additional contracts separately for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in this journal (e.g., publishing in an institutional repository or as a book chapter), with acknowledgment of authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are encouraged to publish and distribute their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their personal page) at any point after the editorial process.
Also, the AUTHOR is informed and consents that the HSJ can incorporate his article into existing or future scientific databases and indexers, under the conditions defined by the latter at all times, which will involve, at least, the possibility that the holders of these databases can perform the following actions on the article.
References
Evans WJ, Morley JE, Argilés J, Bales C, Baracos V, Guttridge D, et al. Cachexia: a new definition. Clin Nutr. 2008;27(6):793-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2008.06.013
Morley JE, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Anker SD. COVID-19: a major cause of cachexia and sarcopenia? J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(4):863-5. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12589
Anker MS, Landmesser U, von Haehling S, Butler J, Coats AJS, Anker SD. Weight loss, malnutrition, and cachexia in COVID-19: facts and numbers. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(1):9-13. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12674
Welch C, Greig C, Masud T, Wilson D, Jackson TA. COVID-19 and acute sarcopenia. Aging Dis. 2020;11(6):1345-51. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2020.1014
Piotrowicz K, Gąsowski J, Michel JP, Veronese N. Post-COVID-19 acute sarcopenia: physiopathology and management. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33(10):2887-98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-021-01942-8
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412-23. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afq034
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afy169
Aryana IGPS, Setiati S, Rini SS. Molecular Mechanism of Acute Sarcopenia in Elderly Patient with COVID - 19. Acta Med Indones. 2021;53(4):481-92.
Cederholm T, Jensen GL, Correia MITD, Gonzalez MC, Fukushima R, Higashiguchi T, et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition - A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019;10(1):207-17. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12383
Allard L, Ouedraogo E, Molleville J, Bihan H, Giroux-Leprieur B, Sutton A, et al. Malnutrition: Percentage and association with prognosis in patients hospitalized for coronavirus disease 2019. Nutrients. 2020;12(12):3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123679
Cava E, Neri B, Grazia M, Riso S, Carbone S. Obesity pandemic during COVID-19 outbreak: Narrative review and future considerations. Clin Nutr. 2021;40:1637-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2021.02.038
Martinez-Ferran M, Guía-Galipienso F de la, Sanchis-Gomar F, Pareja-Galeano H. Metabolic Impacts of Confinement during the COVID-19 Pandemic Due to Modified Diet and Physical Activity Habits. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061549
Izquierdo M, Merchant RA, Morley JE, Anker SD, Aprahamian I, Arai H, et al. International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25(7):824-53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-021-1665-8
Kirwan R, McCullough D, Butler T, Perez de Heredia F, Davies IG, Stewart C. Sarcopenia during COVID-19 lockdown restrictions: long-term health effects of short-term muscle loss. Geroscience. 2020;42(6):1547-78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00272-3
Mautong H, Gallardo-Rumbea JA, Alvarado-Villa GE, Fernández-Cadena JC, Andrade-Molina D, Orellana-Román CE, et al. Assessment of depression, anxiety and stress levels in the Ecuadorian general population during social isolation due to the COVID-19 outbreak: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):212. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-021-03214-1
Clark BC, Carson RG. Sarcopenia and Neuroscience: Learning to Communicate. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2021;76(10):1882-90. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glab098
Ali AM, Kunugi H. Skeletal Muscle Damage in COVID-19: A Call for Action. Medicina (Lithuania). 2021;57(4):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57040372
Cox MC, Booth M, Ghita G, Wang Z, Gardner A, Hawkins RB, et al. The impact of sarcopenia and acute muscle mass loss on long-term outcomes in critically ill patients with intra-abdominal sepsis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(5):1203-13. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12752
Urner M, Mitsakakis N, Vorona S, Chen L, Sklar MC, Dres M, et al. Identifying subjects at risk for diaphragm atrophy during mechanical ventilation using routinely available clinical data. Respir Care. 2021;66(4):551-8. https://doi.org/10.4187/respcare.08223
Brosnahan SB, Jonkman AH, Kugler MC, Munger JS, Kaufman DA. COVID-19 and Respiratory System Disorders: Current Knowledge, Future Clinical and Translational Research Questions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40(11):2586-97. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314515
Schiessel DL, Yamazaki RK, Kryczyk M, Coelho I, Castro D, Yamaguchi AA, et al. Does Oil Rich in Alpha-Linolenic Fatty Acid Cause the Same Immune Modulation as Fish Oil in Walker 256 Tumor-Bearing Rats? Nutr Cancer. 2016;68(8):1369-80. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2016.1224364
Simonnet A, Chetboun M, Poissy J, Raverdy V, Noulette J, Duhamel A, et al. High Prevalence of Obesity in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Requiring Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Obesity. 2020;28(7):1195-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22831
Choe SS, Huh JY, Hwang IJ, Kim JI, Kim JB. Adipose tissue remodeling: Its role in energy metabolism and metabolic disorders. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016;7(APR):30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2016.00030
Ma C, Cong Y, Zhang H. COVID-19 and the Digestive System. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(7):1003-6. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000000691
Soares MN, Eggelbusch M, Naddaf E, Gerrits KHL, van der Schaaf M, van den Borst B, et al. Skeletal muscle alterations in patients with acute Covid-19 and post-acute sequelae of Covid-19. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):11-22. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12896
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181(2):271-280.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Stukalov A, Girault V, Grass V, Karayel O, Bergant V, Urban C, et al. Multilevel proteomics reveals host perturbations by SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 2021;594(7862):246-252. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03493-4
Siddiq MAB, Rathore FA, Clegg D, Rasker JJ. Pulmonary rehabilitation in COVID-19 patients: A scoping review of current practice and its application during the pandemic. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;66(4):480-94. https://doi.org/10.5606/tftrd.2020.6889
Pleguezuelos E, Del Carmen A, Llorensi G, Carcole J, Casarramona P, Moreno E, et al. Severe loss of mechanical efficiency in COVID-19 patients. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(4):1056-63. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12739
Tay MZ, Poh CM, Rénia L, MacAry PA, Ng LFP. The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20(6):363-74. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. The Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1033-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Schiessel DL, Baracos VE. Barriers to cancer nutrition therapy: Excess catabolism of muscle and adipose tissues induced by tumour products and chemotherapy. Proc Nutr Soc. 2018;77(4):394-402. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665118000186
Tuttle CSL, Thang LAN, Maier AB. Markers of inflammation and their association with muscle strength and mass: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;64(April):101185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101185
Alfaro E, Díaz-García E, García-Tovar S, Zamarrón E, Mangas A, Galera R, et al. Upregulated Proteasome Subunits in COVID-19 Patients: A Link with Hypoxemia, Lymphopenia and Inflammation. Biomolecules. 2022;12(3):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030442
Ahmad K, Shaikh S, Ahmad SS, Lee EJ, Choi I. Cross-Talk Between Extracellular Matrix and Skeletal Muscle: Implications for Myopathies. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11(February):142. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00142
Rodriguez B, Branca M, Gutt-Will M, Roth M, Söll N, Nansoz S, et al. Development and early diagnosis of critical illness myopathy in COVID-19 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;(June 2021):1883-95. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12989
Ying L, Zhang Q, Yang YM, Zhou JY. A Combination of Serum Biomarkers in Elderly Patients with Sarcopenia: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Int J Endocrinol. 2022;2022:4026940. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4026940
Asoudeh F, Dashti F, Raeesi S, Heshmat R, Bidkhori M, Jalilian Z, et al. Inflammatory cytokines and sarcopenia in Iranian adults-results from SARIR study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):5471. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09139-3
Ali AM, Kunugi H. Screening for Sarcopenia (Physical Frailty) in the COVID-19 Era. Int J Endocrinol. 2021;2021:5563960. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5563960
Donini LM, Busetto L, Bischoff SC, Cederholm T, Ballesteros-Pomar MD, Batsis JA, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria for sarcopenic obesity: ESPEN and EASO consensus statement. Clinical Nutrition. 2022;41(4):990-1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2021.11.014
Wilkinson TJ, Yates T, Baker LA, Zaccardi F, Smith AC. Sarcopenic obesity and the risk of hospitalization or death from coronavirus disease 2019: findings from UK Biobank. JCSM Rapid Commun. 2022;5(1):3-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/rco2.47
Zhang X, Lewis AM, Moley JR, Brestoff JR. A systematic review and meta-analysis of obesity and COVID-19 outcomes. Scientific Reports - Nature. 2021;11(1):7193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86694-1
Kara M, Ata AM, Özçakar L. Sarcopenic obesity is the real problem in COVID-19 ! Eur J Intern Med. 2021;93(August):103-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2021.08.007
Mentella MC, Scaldaferri F, Gasbarrini A, Miggiano GAD. The role of nutrition in the covid-19 pandemic. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041093
McCarthy C, O'Donnell CP, Kelly NEW, O'Shea D, Hogan AE. COVID-19 severity and obesity: are MAIT cells a factor? Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(5):445-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00140-5
Popkin BM, Du S, Green WD, Beck MA, Algaith T, Herbst CH, et al. Individuals with obesity and COVID-19: A global perspective on the epidemiology and biological relationships. Obes Rev. 2020;21(11):e13128. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13128
Barazzoni R, Bischoff SC, Busetto L, Cederholm T, Schneider S, Singer P, et al. Nutritional management of individuals with obesity and COVID-19: ESPEN expert statements and practical guidance. Clin Nutr. 2021;41(12):2869-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2021.05.006
Higgins V, Sohaei D, Diamandis EP, Prassas I. COVID-19: from an acute to chronic disease? Potential long-term health consequences. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2021;58(5):297-310. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408363.2020.1860895
Anaya J manuel, Rojas M, Salinas ML, Rodríguez Y, Roa G, Lozano M, et al. Post-COVID syndrome. A case series and comprehensive review. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;20(11):102947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102947
Nalbandian A, Sehgal K, Gupta A, Madhavan M V, Mcgroder C, Stevens JS, et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat Med. 2021;27(4):601-15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z
Wong SH, Lui RNS, Sung JJY. Covid-19 and the digestive system. J Gastroenterol Hepatol (Australia). 2020;35(5):744-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.15047
Dahiya DS, Kichloo A, Albosta M, Pagad S, Wani F. Gastrointestinal implications in COVID-19. J Investig Med. 2020;68(8):1397-401. https://doi.org/10.1136/jim-2020-001559
Zuo T, Zhang F, Lui GCY, Yeoh YK, Li AYL, Zhan H, et al. Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients With COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization. Gastroenterol. 2020;159(3):944-955.e8. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048
Liu C, Cheung WH, Li J, Chow SKH, Yu J, Wong SH, et al. Understanding the gut microbiota and sarcopenia: a systematic review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(6):1393-407. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12784
Stachowska E, Folwarski M, Jamioł-Milc D, Maciejewska D, Skonieczna-żydecka K. Nutritional support in coronavirus 2019 disease. Medicina (Lithuania). 2020;56(289):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56060289
Barrea L, Grant WB, Frias-Toral E, Vetrani C, Verde L, de Alteriis G, et al. Dietary Recommendations for Post-COVID-19 Syndrome. Nutrients. 2022;14(6):1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061305
Rogeri PS, Zanella R, Martins GL, Garcia MDA, Leite G, Lugaresi R, et al. Strategies to prevent sarcopenia in the aging process: Role of protein intake and exercise. Nutrients. 2022;14(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010052
Singer P, Blaser AR, Berger MM, Alhazzani W, Calder PC, Casaer MP, et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit. Clin Nutr. 2019;38(1):48-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.037
Narici M, Vito G De, Franchi M, Paoli A, Moro T, Marcolin G, et al. Impact of sedentarism due to the COVID-19 home confinement on neuromuscular, cardiovascular and metabolic health: Physiological and pathophysiological implications and recommendations for physical and nutritional countermeasures. Eur J Sport Sci. 2021;21(4):614-35. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2020.1761076
Ferrara F, de Rosa F, Vitiello A. The Central Role of Clinical Nutrition in COVID-19 Patients During and After Hospitalization in Intensive Care Unit. SN Compr Clin Med. 2020;2(8):1064-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-020-00410-0
Ko CH, Wu SJ, Wang ST, Chang YF, Chang CS, Kuan TS, et al. Effects of enriched branched-chain amino acid supplementation on sarcopenia. Aging. 2020;12(14):15091-103. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103576
Pallath MM, Ahirwar AK, Tripathi SC, Asia P, Sakarde A, Gopal N. COVID-19 and nutritional deficiency: A review of existing knowledge. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2021;42(1):77-85. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2020-0074
Angelidi AM, Kokkinos A, Katechaki E, Ros E, Mantzoros CS. Mediterranean diet as a nutritional approach for COVID-19. Metabolism. 2020;114:154407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154407
Iddir M, Brito A, Dingeo G, Del Campo SSF, Samouda H, La Frano MR, et al. Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: Considerations during the covid-19 crisis. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061562
Gasmi A, Tippairote T, Mujawdiya PK, Peana M, Menzel A, Dadar M, et al. The microbiota-mediated dietary and nutritional interventions for COVID-19. Clinical Immunology. 2021;226:108725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2021.108725