Serum levels of antioxidants and its supplementation in people living with HIV: integrative review
Main Article Content
Abstract
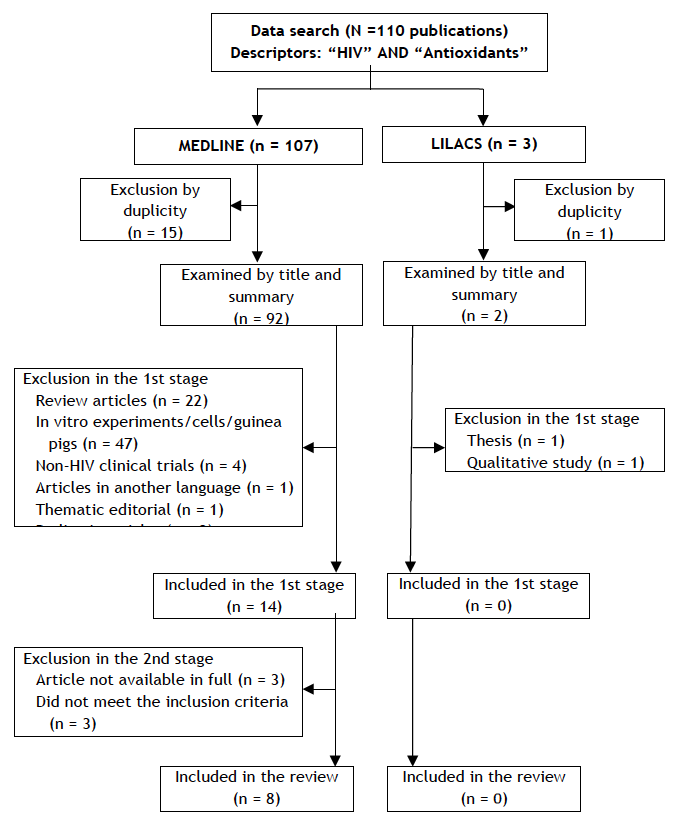
Objective: To conduct an integrative review of serum levels of antioxidants and the effects of their supplementation on people living with HIV (PLHIV). Methods: A research was performed in the electronic databases LILACS and MEDLINE, using the descriptors "HIV" AND "antioxidants"; 110 publications were identified, 92 of which were available in the MEDLINE database and 3 in the LILACS database. After applying the exclusion criteria, 8 articles were selected for final evaluation.Results: The studies selected for the review were divided into 4 prospective observational studies and 4 clinical trials with supplementation of antioxidants or food sources of antioxidants. We observed that the initiation of antiretroviral therapy and its prolonged use negatively influenced the parameters of oxidative stress, and that deficiency of antioxidants was associated with more significant damage to mitochondrial DNA. Supplementation of foods that are sources of antioxidants, such as dark chocolate and spirulina, has had beneficial effects on serum lipids and antioxidant capacity. Conclusion: Clinical trials with a more robust methodology, supplementation of isolated nutrients, for more extended periods of intervention, and with the assessment of food consumption are necessary to elucidate their effects on oxidative stress in PLHIV faced with factors such as the use of antiretroviral therapy and changes in metabolic rates of this population.
Article Details
Authors maintain copyright and grant the HSJ the right to first publication. From 2024, the publications wiil be licensed under Attribution 4.0 International 
 , allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
, allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are authorized to assume additional contracts separately for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in this journal (e.g., publishing in an institutional repository or as a book chapter), with acknowledgment of authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are encouraged to publish and distribute their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their personal page) at any point after the editorial process.
Also, the AUTHOR is informed and consents that the HSJ can incorporate his article into existing or future scientific databases and indexers, under the conditions defined by the latter at all times, which will involve, at least, the possibility that the holders of these databases can perform the following actions on the article.
References
Silva MM. Polimorfismo da região do Fator de Necrose Tumoral (TNF) na síndrome da lipodistrofia associada à terapia anti-retroviral em portadores do HIV-1 [Dissertação de Mestrado]. Ribeirão Preto, SP: Curso de Enfermagem, Escola de Enfermagem de Ribeirão Preto, Universidade de São Paulo; 2008. 154 p.
Deresz LF, Lazzarotto AR, Manfroi WC, Gaya A, Sprinz E, Oliveira AR, et al. O estresse oxidativo e o exercício físico em indivíduos HIV positivo. Rev Bras Med Esporte. 2007;13(4):275-9. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-86922007000400013
Louie JK, Hsu LC, Osmond DH, Katz MH, Schwarcz SK. Trends in causes of death among persons with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy, San Francisco, 1994-1998. J Infect Dis. 2002;186(7):1023-7. https://doi.org/10.1086/343862 PMid:12232845
Meng Q, Lima JAC, Lai H, Vlahov D, Celentano DD, Strathdee SA, et al. Coronary artery calcification, atherogenic lipid changes, and increased erythrocyte volume in black injection drug users infected with human immunodeficiency virus-1 treated with protease inhibitors. Am Heart J. 2002;144(4):642-8. https://doi.org/10.1067/mhj.2002.125009 PMID:12360160
UNAIDS. Communities at the Centre Global AIDS Update 2019 [Internet]. [cited 2021 May 2]. Avaiable from: https://bit.ly/3aTcsNg
Mankal PK, Kotler DP. From wasting to obesity, changes in nutritional concerns in HIV/AIDS. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2014;43(3):647-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2014.05.004 PMid:25169559
Kotler DP, Wang J, Pierson RN. Body composition studies in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985;42(6):1255-65. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/42.6.1255 PMid:3865530
Shivakoti R, Christian P, Yang WT, Gupte N, Mwelase N, Kanyama C, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of micronutrient deficiencies pre- and post-antiretroviral therapy (ART) among a diverse multicountry cohort of HIV-infected adults. Clin Nutr. 2016;35(1):183-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2015.02.002 PMid:25703452 PMCid:PMC4531105
Drain PK, Kupka R, Mugusi F, Fawzi MW. Micronutrients in HIV-positive persons receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;85(2):333-45. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/85.2.333 PMid:17284727
Tang AM, Lanzilloti J, Hendricks K, Gerrior J, Ghosh M, Woods M, et al. Micronutrients: current issues for HIV care providers. AIDS. 2005;19(9):847-61. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aids.0000171398.77500.a9 PMid:15905665
Kumar S, Sharma S, Vadesuva N. Review on antioxidants and evaluation procedures. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-017-2414-z PMID: 28986809
Barbosa KBF, Costa NMB, Alfenas RCG, Paula SO, Minim VPR, Bressan J. Estresse oxidativo: conceito, implicações e fatores modulatórios. Rev Nutr. 2010;23(4):629-43. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-52732010000400013
Sharma B. Oxidative stress in HIV patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. Curr HIV Res. 2014;12(1):13-21. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570162X12666140402100959 PMid:24694264
Day BJ, Lewis W. Oxidative stress in NRTI-induced toxicity: evidence from clinical experience and experiments in vitro and in vivo. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2004;3(4):207-16. https://doi.org/10.1385/ct:4:3:207 PMID:15470269
Richardson WS, Wilson MC, Nishikawa J, Hayward RS. The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP J Club. 1995;123(3):A12-3. PMID: 7582737
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O'Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467-73. https://doi.org/10.7326/m18-0850 PMID:30178033
Makinde O, Rotimi K, Ikumawoyi V, Adeyemo T, Olayemi S. Effect of vitamin A and vitamin C supplementation on oxidative stress in HIV and HIV-TB co-infection at Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH) Nigeria. Afr Health Sci. 2017;17(2):308-14. https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v17i2.3 PMid:29062324 PMCid:PMC5637014
Tasca KI, Caleffi JT, Correa CR, Gatto M, Tavares FC, Camargo CC, et al. Antiretroviral therapy initiation alters the redox system of asymptomatic HIV-infected individuals: a longitudinal study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017: 9834803. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9834803 PMid:28421130 PMCid:PMC5379093
Martinez SS, Campa A, Li Y, Fleetwood C, Stewart T, Ramamoorthy V, et al. Low plasma zinc is associated with higher mitochondrial oxidative stress and faster liver fibrosis development in the miami adult studies in HIV cohort. J Nutr. 2017;147(4):556-62. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.116.243832 PMid:28228506 PMCid:PMC5368586
Watanabe LM, Junior FB, Jordão AA, Navarro AM. Influence of HIV infection and the use of antiretroviral therapy on selenium and selenomethionine concentrations and antioxidant protection. Nutrition. 2016;32(11-12):1238-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2016.03.024 PMid:27255831
Petrilli A, Souza SJ, Teixeira AM, Pontilho PM, Souza JMP, Luzia LA, et al. Effect of chocolate and yerba mate phenolic compounds on inflammatory and oxidative biomarkers in HIV/AIDS individuals. Nutrients. 2016;8(5):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8050132 PMid:27223302 PMCid:PMC4882654
Ly J, lagman M, Saing T, Singh MK, Tudela EV, Morris D, et al. Liposomal glutathione supplementation restores TH1 Cytokine response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in HIV-infected individuals. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015;35(11):875-87. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2014.0210 PMid:26133750 PMCid:PMC4642835
Ande A, McArthur C, Ayuk L, Awasom C, Achu PN, Njinda A, et al. Effect of mild-to-moderate smoking on viral load, cytokines, oxidative stress, and cytochrome P450 enzymes in HIV-infected individuals. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0122402. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122402 PMid:25879453 PMCid:PMC4399877
Winter F, Emakan F, Kfutwah A, Hermann J, Azabji-Kenfack M, Krawinkel MB. The effect of Arthrospira platensis capsules on CD4 T-Cells and antioxidative capacity in a randomized pilot study of adult women infected with human immunodeficiency virus not under HAART in Yaoundé, Cameroon. Nutrients. 2014;6(7):2973-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6072973 PMid:25057105 PMCid:PMC4113773
World Health Organization. Update of recommendations on first- and second-line antiretroviral regimens. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2019 [cited 2021 May 2] (WHO/CDS/HIV/19.15). Avaiable from: https://bit.ly/3edhG8G