Assessment of functional balance in children with sensory impairments undergoing hippotherapy
Main Article Content
Abstract
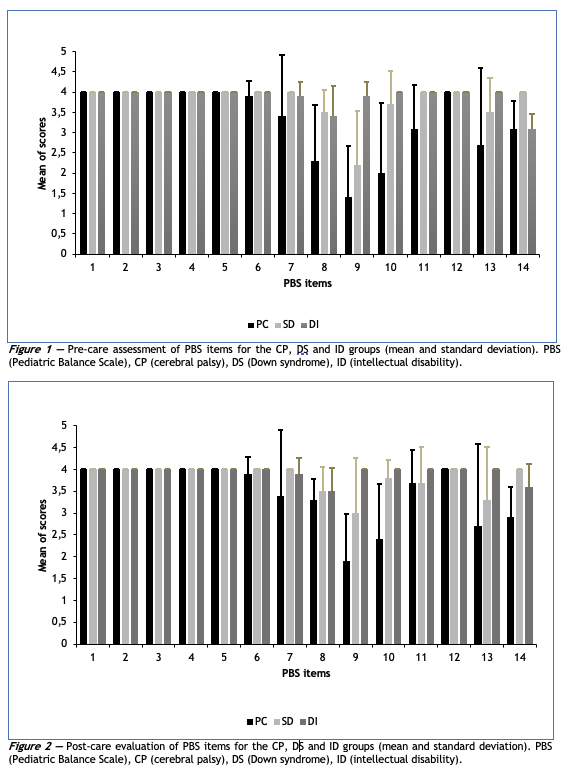
Objective: To evaluate the functional balance of children with sensory impairments submitted to hippotherapy. Methods: 24 children of both genres equally participated in three groups: cerebral palsy (CP), Down syndrome (DS), and intellectual disability (ID) with the respective age groups (10.71 ± 2.69 years), (12.83 ± 2.64 years), and (11 ± 1.69 years).There were 15 attendances in hippotherapy with riding materials specific to each group. The Pediatric Balance Scale (EEP) was used before the 1st and after the 15th hippotherapy session (pre and post moments) to assess functional balance. The data were analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk tests (normality), Bartlett test (homogeneity), and, between the pre- and post-care times, the paired t-test (intra-groups) and ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison tests (between groups), with statistical significance for p < 0.05. Results: in the post-attendance, there was an increase in the EEP score for the three groups (intra groups) with significance for children with ID (p = 0.003) and DS (p = 0.033); the CP group had a lower score (inter groups) in both times, pre (p = 0.003) and post (p = 0.002) attendance. Conclusion: hippotherapy contributed to the functional balance of children with distinct sensory impairments, according to the clinical diagnosis and riding material specific to the group, thus being able to be considered a therapeutic method with relevant benefits regarding the sensory aspects of the population.
Article Details
Authors maintain copyright and grant the HSJ the right to first publication. From 2024, the publications wiil be licensed under Attribution 4.0 International 
 , allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
, allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are authorized to assume additional contracts separately for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in this journal (e.g., publishing in an institutional repository or as a book chapter), with acknowledgment of authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are encouraged to publish and distribute their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their personal page) at any point after the editorial process.
Also, the AUTHOR is informed and consents that the HSJ can incorporate his article into existing or future scientific databases and indexers, under the conditions defined by the latter at all times, which will involve, at least, the possibility that the holders of these databases can perform the following actions on the article.
References
Kleiner AFR, Schlittler DXC, Sánchez-Arias MDR. O papel dos sistemas visual, vestibular, somatosensorial e auditivo para o controle postural. Rev Neurocienc. 2011;19(2):349-57. https://doi.org/10.34024/rnc.2011.v19.8382
Sibley KM, Beauchamp MK, Van Ooteghem K, Straus SE, Jaglal SB. Using the systems framework for postural control to analyze the components of balance evaluated in standardized balance measures: a scoping review. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2015;96(1):122-132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2014.06.021 PMid:25073007
Victorio LVG, Fujisawa DS. Influence of age, sex, and visual information on postural control in children. Motriz: J Phys Ed. 2019;25(1):e101978. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1980-6574201900010017
Sá CDSC, Boffino CC, Ramos RT, Tanaka C. Development of postural control and maturation of sensory systems in children of different ages a cross-sectional study. Braz J Phys Ther. 2018;22(1):70-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjpt.2017.10.006 PMid:29239806 PMCid:PMC5816079
Rosenbaum P. Cerebral palsy: is the concept still viable? Dev Med Child Neurol. 2017;59(6):564. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13418 PMid:28463457
Malak R, Kostiukow A, Krawczyk-Wasielewska A, Mojs E, Samborski W. Delays in motor development in children with Down syndrome. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1904-10. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.893377 PMid:26132100 PMCid:PMC4500597
Martinez-Morga M, Martinez S. Plasticidad neural: la sinaptogenesis durante el desarrollo normal y su implicacion en la discapacidad intelectual. Rev Neurol. 2017;64(Suppl. 1):S0-50. https://doi.org/10.33588/rn.64S01.2017048
APA. American Psychiatric Association. Manual diagnóstico e estatístico de transtornos mentais. DSM-5. Porto Alegre: Artmed; 2014.
ANDE-Brasil. Associação Nacional de Equoterapia [Internet]. [accessed 2021 May 6]. Available from: http://equoterapia.org.br
Wood WH, Fields BE. Hippotherapy: a systematic mapping review of peer-reviewed research, 1980 to 2018. Disabil Rehabil. 2019;6:1-25. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2019.1653997 PMid:31491353
Tauffkirchen E. Hippotherapie. In: Lohse-Busch H., Riedel M., Graf-Baumann T. (eds) Das therapeutische Angebot für bewegungsgestörte Kinder. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2001. pp. 81-99. Avaiable from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-59567-7_9
Spink J. Developmental riding therapy: a team approach to assessment and treatment. Pediatric Physical Therapy. 1994;6(4):223. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001577-199400640-00023
Uchiyama H, Ohtani N, Ohta M. Three-dimensional analysis of horse and human gaits in therapeutic riding. Appl Anim Behav Sci. 2011;135(4):271-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2011.10.024
Diniz LH, Mello EC, Ribeiro MF, Lage JB, Bevilacqua Júnior DE, Ferreira AA, et al. Impact of hippotherapy for balance improvement and flexibility in elderly people. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2020;24(2):92-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbmt.2019.10.002 PMid:32507159
Araujo TB, Martins WR, Freitas MP, Camargos E, Mota J, Safons MP. An exploration of equine-assisted therapy to improve balance, functional capacity, and cognition in older adults with Alzheimer disease. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2019;42(3):E155-60. https://doi.org/10.1519/JPT.0000000000000167 PMid:29630005
Costa JVL, Serrão Júnior NF, Luvizutto GJ, Araujo TB, Safons MP, Rezende ALG. Efeitos da equoterapia sobre o equilíbrio estático e dinâmico no transtorno neurocognitivo maior ou leve devido à Doença de Huntington. Fisioter Bras. 2018;19(2):215-22. https://doi.org/10.33233/fb.v19i2.2131
Costa VSF, Silva HM, Azevêdo M, Silva AR, Cabral LLP, Barros JF. Effect of hippotherapy in the global motor coordination in individuals with Down Syndrome. Fisioter Mov. 2017;30(Suppl.1):229-40. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5918.030.s01.ao22
Stergiou A, Tzoufi M, Ntzani E, Varvarousis D, Beris A, Ploumis A. therapeutic effects of horseback riding interventions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;96(10):717-25. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0000000000000726 PMid:28252520
Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Bartlett D, Livingston M. GMFCS – E & R. Sistema de Classificação da Função Motora Grossa (brazilian version) (translated by Silva DBR, Pfeifer LI, Funayama CAR). CanChild Centre for Childhood Disability Research. 2007 [cited 2021 May 7]:1-6. Available from: https://bit.ly/3xPkOPU
Lage JB, Ribeiro MF, Teixeira VPA, Rosa RC, Ferreira AA, Espindula AP. Effect of horse riding equipment in activity of trunk and lower limb muscles in equine-assisted therapy. Acta Sci Health Sci. 2020;42:e52739. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascihealthsci.v42i1.52739
Ries LGK, Michaelsen SM, Soares PSA, Monteiro VC, Allegretti KMG. Cross-cultural adaptation and reliability analysis of the Brazilian version of Pediatric Balance Scale (PBS). Rev Bras Fisioter. 2012;16(3):205-15. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-35552012005000026 PMid:22699691
Uzun ALL. Equoterapia: aplicação em distúrbios do equilíbrio. São Paulo: Vetor, 2005.
Oliveira Junior E, Soeth PR, Paixão AFV, Antunes FD. equilíbrio postural em crianças com deficiência intelectual. J Health Sci [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2021 May 7];20(2):140-5. Avaiable from: https://bit.ly/3eqetCJ
Ambrozy T, Mazur-Rylska A, Chwała W, Ambrozy D, Mucha T, Omorczyk J, et al. The role of hippotherapeutic exercises with larger support surface in development of balance in boys aged 15 to 17 years with mild intellectual disability. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2017;19(4):143-51. https://doi.org/10.5277/ABB-00776-2016-04
Dupre C, Weidman-Evans E. Musculoskeletal development in patients with Down syndrome. JAAPA. 2017;30(12):38-40. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.JAA.0000526779.77230.79 PMid:29210907
Oliveira LS, Golin MO. Técnica para redução do tônus e alongamento muscular passivo: efeitos na amplitude de movimento de crianças com paralisia cerebral espástica. ABCS Health Sci. 2017;42(1):27-33. https://doi.org/10.7322/abcshs.v42i1.946
Graham HK, Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Dan B, Lin JP, Damiano DL, et al. Cerebral palsy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:15082. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.82 PMid:27188686
Leite JC, Neves JCJ, Victor LGV, Fujisawa DS. Evaluation of postural control in children and adolescents with Down Syndrome aged eight to twelve years old. J Hum Growth Dev. 2018;28(1):50-7. https://doi.org/10.7322/jhgd.127335
Trindade AS, Nascimento MA. Avaliação do desenvolvimento motor em crianças com Síndrome de Down. Rev Bras Ed Esp. 2016;22(4):577-88. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1413-65382216000400008
Van Der Krogt MM, Bar-On L, Kindt T, Desloovere K, Harlaar J. Neuro-musculoskeletal simulation of instrumented contracture and spasticity assessment in children with cerebral palsy. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016;13(1):64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-016-0170-5 PMid:27423898 PMCid:PMC4947289
Beinotti F, Correia N, Christofoletti G, Borges G. Use of hippotherapy in gait training for hemiparetic post-stroke. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2010;68(6):908-13. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0004-282X2010000600015 PMid:21243251
Pedebos BM, Porto LB, Copetti F, Balk RS. Avaliação do controle postural e sua relação com o hemisfério acometido em pacientes com acidente vascular cerebral praticando equoterapia. Fisioter Bras [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2021 May 7];15(1):22-8. Avaiable from: https://bit.ly/3vPSqLU
Araújo TB, Martins WR, Blasczyk JC, Feng YH, Oliveira RI, Copetti F, et al. Efeito da equoterapia no equilíbrio de idosos: uma revisão sistemática com metanálise. R Bras Ci Mov [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2021 May 7];26(3):178-84. Avaiable from: https://bit.ly/3o6d9IJ
Kwon JY, Chang HJ, Lee JY, Ha Y, Lee PK, Kim Y-H. Effects of hippotherapy on gait parameters in children with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;92:774-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2010.11.031 PMid:21530725
Okamoto K, Nagai T, Miyawaki A, Hayashi Y. Rapid and persistent modulation of actin dynamics regulates postsynaptic reorganization underlying bidirectional plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:1104-12. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1311 PMid:15361876