Cardiac autonomic activity, endothelial function and physical fitness in type 2 diabetic patients
Main Article Content
Abstract
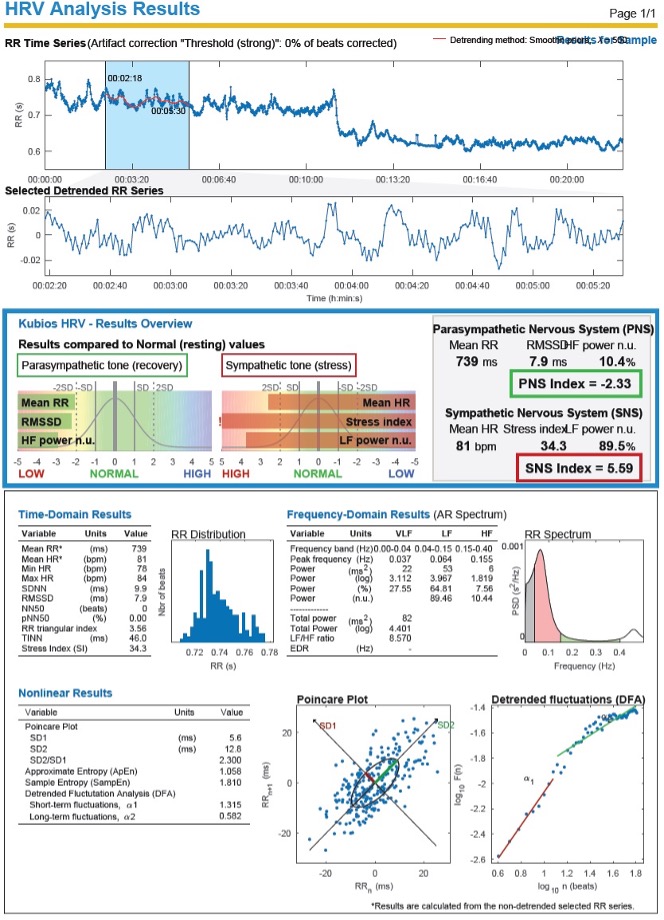
Objective: To investigate the association between cardiac autonomic activity, endothelial function, and physical fitness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Methods: Twenty-seven patients with T2DM were studied, with a mean age of 57 ± 9 years and a mean disease duration of 7.4 ± 5 years. The assessment of physical fitness was performed using the Shuttle Walking Test (SWT), cardiac autonomic modulation by heart rate variability (HRV), and endothelial function was assessed by flow-mediated dilation (FMD) of the brachial artery through ultrasound imaging. Results: The main finding of this study was that some HRV indices (SDNN, RMSSD, and HF) were significantly correlated with endothelial function in individuals with T2DM, with R values between 0.51 and 0.57 (p < 0, 05), for all relationships. Additionally, an association was found between the distance covered in the SWT and the basal diameter of the brachial artery (R = 0.59; p = 0.01). Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that some HRV indices are associated with DMF, indicating an interaction between these two systems. Furthermore, our findings suggest a correlation between physical fitness and endothelial function in individuals with T2DM.
Article Details
Authors maintain copyright and grant the HSJ the right to first publication. From 2024, the publications wiil be licensed under Attribution 4.0 International 
 , allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
, allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are authorized to assume additional contracts separately for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in this journal (e.g., publishing in an institutional repository or as a book chapter), with acknowledgment of authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are encouraged to publish and distribute their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their personal page) at any point after the editorial process.
Also, the AUTHOR is informed and consents that the HSJ can incorporate his article into existing or future scientific databases and indexers, under the conditions defined by the latter at all times, which will involve, at least, the possibility that the holders of these databases can perform the following actions on the article.
References
Stanford KI, Goodyear LJ. Exercise and type 2 diabetes: molecular mechanisms regulating glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Adv Physiol Educ. 2014;38(4):308-14. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.00080.2014
Bertoluci MC, Rocha VZ. Cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2017;9:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-017-0225-1
Pimentel I. Taxa de incidencia de diabetes cresceu 61,8% nos ultimos 10 anos [Internet]. Manguinhos (RJ): Fiocruz; 2018 Feb 2 [cited 2022 Ago 18]. Available from: https://bit.ly/3A2Or24
Jacob G, Costa F, Biaggioni I. Spectrum of autonomic cardiovascular neuropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(7):2174-80. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.7.2174
Vinik AI, Ziegler D. Diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Circulation. 2007;115(3):387-97. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.634949
Kang SJ, Ko KJ, Baek UH. Effects of 12 weeks combined aerobic and resistance exercise on heart rate variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(7):2088-93. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.28.2088
Aubert AE, Seps B, Beckers F. Heart rate variability in athletes. Sports Med. 2003;33(12):889-919. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200333120-00003
De Angelis K, Santos MSB, Irigoyen MC. Sistema nervoso autônomo e doença cardiovascular. Rev Soc Cardiol Rio Grande do Sul [Internet]. 2004 [cited 2022 Aug 18];3:1-7. Available from: https://bit.ly/3zWCjja
Maser RE, Mitchell BD, Vinik AI, et al. The association between cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and mortality in individuals with diabetes: a metaanalysis. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(6):1895-901. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.6.1895
Brassard P, Ferland A, Bogaty P, Desmeules M, Jobin J, Poirier P. Influence of glycemic control on pulmonary function and heart rate in response to exercise in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2006;55(11):1532-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2006.06.025
Vincent A, Edwards J, McLean L, Hong Y, Cerri F, Lopez I, Quattrini A, Feldman EL. Mitochondrial biogenesis and fission in axons in cell culture and animal models of diabetic neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;120(4):477-89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0697-7
Góralczyk K, Szymańska J, Szot K, Fisz J, Rość D. Low-level laser irradiation effect on endothelial cells under conditions of hyperglycemia. Lasers Med Sci. 2016;31(5):825-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-1880-4
Gibbs BB, Dobrosielski DA, Bonekamp S, Stewart KJ, Clark JM. A randomized trial of exercise for blood pressure reduction in type 2 diabetes: effect on flow-mediated dilation and circulating biomarkers of endothelial function. Atherosclerosis. 2012;224(2):446-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.07.035
Ramos JS, Dalleck LC, Tjonna AE, Beetham KS, Coombes JS. The impact of high intensity interval training versus moderate intensity continuous training on vascular function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015;45(5):679-92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-015-0321-z
Gambassi BB, Almeida FJF, Almeida AEAF, Ribeiro DAF, Gomes RSA, Chaves LFC, et al. Acute response to aerobic exercise on autonomic cardiac control of patients in phase III of a cardiovascular rehabilitation program following coronary artery bypass grafting. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;34(3):305-10. https://doi.org/10.21470/1678-9741-2019-0030
Singh SJ, Morgan MD, Scott S, Walters D, Hardman AE. Development of a shuttle walking test of disability in patients with chronic airways obstruction. Thorax. 1992;47(12):1019-24. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.47.12.1019
Vanderlei LCM, Pastre CM , Hoshi RA , Carvalho TD , Godoy MF. Noções básicas de variabilidade da frequência cardíaca e sua aplicabilidade clínica. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2009;24(2):205-17. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-76382009000200018
Thijssen DH, Black MA, Pyke KE, Padilla J, Atkinson G, Harris RA, Parker B, Widlansky ME, Tschakovsky ME, Green DJ. Assessment of flow-mediated dilation in humans: a methodological and physiological guideline. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300(1):H2-12. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00471.2010
Madsen SM, Thorup AC, Overgaard K, Bjerre M, Jeppesen PB. Functional and structural vascular adaptations following 8 weeks of low volume high intensity interval training in lower leg of type 2 diabetes patients and individuals at high risk of metabolic syndrome. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2015;121(5):178-86. https://doi.org/10.3109/13813455.2015.1087033
Stirban A, Laude D,Elghozi JL, Sander D, Agelink MW, Hilz MJ, Ziegler D. Acute effects of sildenafil on flow mediated dilatation and cardiovascular autonomic nerve function in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009;25(2):136-43. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.921
Fakhrzadeh H, Yamini-Sharif A, Sharifi F, Tajalizadekhoob Y, Mirarefin M, Mohammadzadeh M, et al. Cardiac autonomic neuropathymeasured by heart rate variability andmarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in early type 2 diabetes. ISRN Endocrinol. 2012;2012:168264. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/168264
Sucharita S, Bantwal G, Idiculla J, Ayyar V, Vaz M. Autonomic nervous system function in type 2 diabetes using conventional clinical autonomic tests, heart rate and blood pressure variability measures. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2011;15(3):198-203. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.83406
Khatoon N, Kumar B, Hazari M. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int J Pharma Bio Sci. 2010;1(3):1-7.
Lellamo F, Tesauro M, Rizza S, Aquilani S, Cardillo C, Iantorno M, et al. Concomitant impairment in endothelial function and neural cardiovascular regulation in offspring of type 2 diabetic subjects. Hypertension. 2006;48(3):418-23. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000234648.62994.ab
Watanabe S, Amiya E, Watanabe M, Takata M, Ozeki A, Watanabe A, et al. Simultaneous heart rate variability monitoring enhances the predictive value of flow-mediated dilation in ischemic heart disease. Circ J. 2013;77(4):1018-25. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-12-1043
Pinter A, Horvath T, Sarkozi A, Kollai M. Relationship between heart rate variability and endothelial function in healthy subjects. Auton Neurosci. 2012;169(2):107-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2012.05.005
Carlson SH, Wyss JM. Neurohormonal regulation of the sympathetic nervous system: new insights into central mechanisms of action. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2008;10(3):233-40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-008-0044-8
Hagg U, Wandt B, Bergstrom G, Volkmann R, Gan LM. Physical exercise capacity is associated with coronary and peripheral vascular function in healthy young adults. Am J Physiol Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005;289(4):H1627-34. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00135.2005