Quality, reliability, and content of YouTube videos in Portuguese language about dental trauma
Conteúdo do artigo principal
Resumo
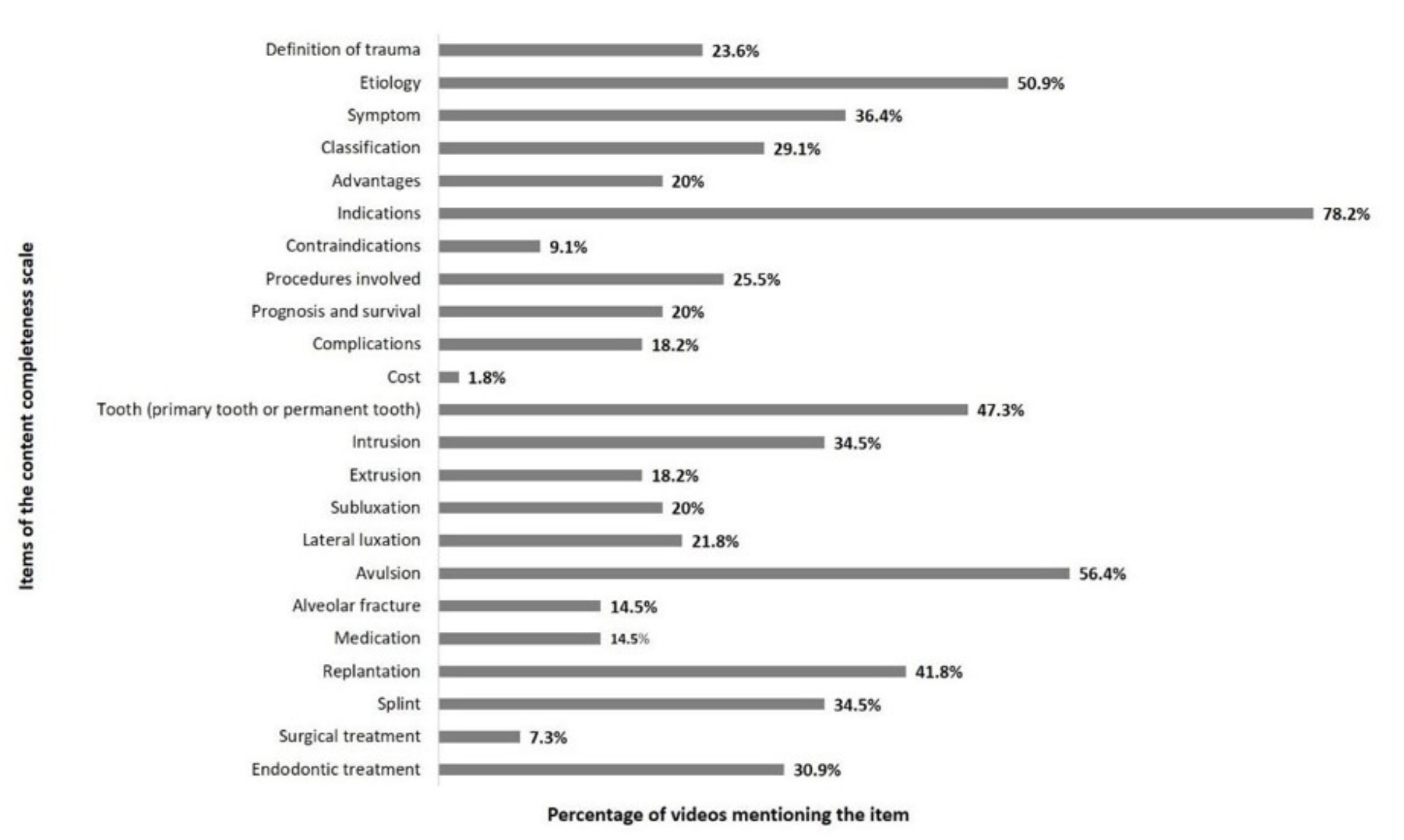
Objective: To evaluate the quality, reliability and content of YouTube videos in Portuguese about dental trauma. Method: An infodemiological study was developed in which the first 60 videos found on YouTube with the terms “dental traumatism”, “dental trauma” and “broken tooth” were analyzed. Repeated videos, longer than one hour, in a language other than Portuguese, not intended for the lay public, resolution of questions, songs, interviews, shorts, and other subjects were excluded. The content of the videos was rated using a 23-point scale that classified them into low, moderate, and high content. Reliability was assessed using the modified DISCERN scale and the overall quality was assessed using the Global Quality Score (GQS) scale. The numbers of likes, dislikes, comments and engagement were also accounted. Data were analyzed by Mann-Whitney and Spearman’s correlation test (α= 5%). Result: A total of 55 videos were included in the study. Most were posted by healthcare professionals (92.7%) and just over half (63.7%) were of good overall quality. There were moderate, positive, and statistically significant correlations between DISCERN and GQS scores (r=0.454), duration (r=0.575), and trauma content (r=0.510). Overall quality correlated moderately, positively, and significantly with content scores (r=0.604) and video length (r=0.467). Conclusion: A significant proportion of Portuguese videos on YouTube about dental trauma had low content, quality and reliability information.
Detalhes do artigo
Os autores mantêm os direitos autorais e concedem ao HSJ o direito de primeira publicação. A partir de 2024, as publicações serão licenciadas sob a Attribution 4.0 International 
 , permitindo seu compartilhamento, reconhecendo a autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
, permitindo seu compartilhamento, reconhecendo a autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
Os autores estão autorizados a assumir contratos adicionais separadamente para distribuição não exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (por exemplo, publicação em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
Os autores são incentivados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho on-line (por exemplo, em repositórios institucionais ou em sua página pessoal) a qualquer momento após o processo editorial.
Além disso, o AUTOR fica informado e consente que o HSJ possa incorporar seu artigo em bases de dados e indexadores científicos existentes ou futuros, nas condições definidas por estes a cada momento, o que envolverá, pelo menos, a possibilidade de que os titulares de esses bancos de dados podem executar as seguintes ações no artigo.
Referências
Milani AJ, Castilho T, Assaf AV, Antunes LS, Antunes LAA. Impact of traumatic dental injury treatment on the Oral Health-Related Quality of Life of children, adolescents, and their family: systematic review and meta-analysis. Dent Traumatol. 2021;37(6):735-48. http://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12697. PMid:34156753. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12697
Levin L, Day PF, Hicks L, O’Connell A, Fouad AF, Bourguignon C, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: general introduction. Dent Traumatol. 2020;36(4):309-13. http://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12574. PMid:32472740. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12574
Vieira WA, Pecorari VGA, Figueiredo-de-Almeida R, Carvas N Jr, Vargas-Neto J, Santos ECA, et al. Prevalence of dental trauma in Brazilian children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cad Saude Publica. 2021;37(12):e00015920. http://doi.org/10.1590/0102-311x00015920. PMid:34909926. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/0102-311x00015920
Internet World Stats [Internet]. Bogota: Miniwatts Marketing Group; 2023 [cited 2023 Aug 10]. Available from: https://www. internetworldstats.com/
Bora K, Das D, Barman B, Borah P. Are Internet videos useful sources of information during global public health emergencies? A case study of YouTube videos during the 2015-16 Zika virus pandemic. Pathog Glob Health. 2018;112(6):320-8. http://doi. org/10.1080/20477724.2018.1507784. PMid:30156974. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/20477724.2018.1507784
Farnood A, Johnston B, Mair FS. A mixed methods systematic review of the effects of patient online self-diagnosing in the ‘smart-phone society’ on the healthcare professional-patient relationship and medical authority. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020;20(1):253. http://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-020-01243-6. PMid:33023577. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-020-01243-6
Li M, Yan S, Yang D, Li B, Cui W. YouTube™ as a source of information on food poisoning. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):952. http://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7297-9. PMid:31311523. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7297-9
Hawryluk NM, Stompór M, Joniec EZ. Concerns of quality and reliability of educational videos focused on frailty syndrome on YouTube platform. Geriatrics. 2021;7(1):3. http://doi. org/10.3390/geriatrics7010003. PMid:35076501. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010003
Ozsoy-Unubol T, Alanbay-Yagci E. YouTube as a source of information on fibromyalgia. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021;24(2):197- 202. http://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.14043. PMid:33355406. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.14043
Korkmaz YN, Buyuk SK. YouTube as a Patient-Information Source for Cleft Lip and Palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2020;57(3):327- 32. http://doi.org/10.1177/1055665619866349. PMid:31362515. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1055665619866349
Hutchison CM, Cave V, Walshaw EG, Burns B, Park C. YouTube™ as a source for patient education about the management of dental avulsion injuries. Dent Traumatol. 2020;36(2):207-11. http://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12517. PMid:31606932. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12517
Ramadhani A, Zettira Z, Rachmawati YL, Hariyani N, Maharani DA. Quality and reliability of halitosis videos on YouTube as a source of information. Dent J. 2021;9(10):120. http://doi. org/10.3390/dj9100120. PMid:34677182. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9100120
Tozar KN, Yapıcı Yavuz G. Reliability of information on YouTube™ regarding pediatric dental trauma. Dent Traumatol. 2021;37(6):772- 8. http://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12708. PMid:34289239. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12708
Google Trends [Internet]. Mountain View: Google Inc.; 2024 [cited 2024 Feb 15]. Available from: https://trends.google.com. br/trends/?geo=BR
Kılınç DD, Sayar G. Assessment of reliability of YouTube videos on orthodontics. Turk J Orthod. 2019;32(3):145-50. http://doi. org/10.5152/TurkJOrthod.2019.18064. PMid:31565689. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5152/TurkJOrthod.2019.18064
Bulman JS, Osborn JF. Measuring diagnostic consistency. Br Dent J. 1989;166(10):377-81. http://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.4806849. PMid:2736171. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.4806849
Souza AC, Alexandre NMC, Guirardello EB. Psychometric properties in instruments evaluation of reliability and validity. Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2017;26(3):649-59. http://doi. org/10.5123/S1679-49742017000300022. PMid:28977189. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5123/S1679-49742017000300022
Logullo P, Torloni MR, Latorraca COC, Riera R. The Brazilian Portuguese version of the DISCERN instrument: translation procedures and psychometric properties. Value Health Reg Issues. 2019;20:172-9. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.vhri.2019.09.001. PMid:31622803. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vhri.2019.09.001
Charnock D, Shepperd S, Needham G, Gann R. DISCERN: an instrument for judging the quality of written consumer health information on treatment choices. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1999;53(2):105-11. http://doi.org/10.1136/jech.53.2.105. PMid:10396471. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.53.2.105
Bernard A, Langille M, Hughes S, Rose C, Leddin D, Veldhuyzen van Zanten S. A systematic review of patient inflammatory bowel disease information resources on the World Wide Web. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102(9):2070-7. http://doi. org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01325.x. PMid:17511753. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01325.x
Day PF, Flores MT, O’Connell AC, Abbott PV, Tsilingaridis G, Fouad AF, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 3. Injuries in the primary dentition. Dent Traumatol. 2020;36(4):343-59. http://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12576. PMid:32458553. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12576
Pons-Fuster E, Ruiz Roca J, Tvarijonaviciute A, López-Jornet P. YouTube information about diabetes and oral healthcare. Odontology. 2020;108(1):84-90. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10266- 019-00445-3. PMid:31396751. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-019-00445-3
Leong AY, Sanghera R, Jhajj J, Desai N, Jammu BS, Makowsky MJ. Is YouTube useful as a source of health information for adults with type 2 diabetes? A South Asian perspective. Can J Diabetes. 2018;42(4):395-403.e4. http://doi.org/10.1016/j. jcjd.2017.10.056. PMid:29282200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjd.2017.10.056
Fernandez-Llatas C, Traver V, Borras-Morell JE, Martinez- Millana A, Karlsen R. Are health videos from hospitals, health organizations, and active users available to health consumers? An analysis of diabetes health video ranking in YouTube. Comput Math Methods Med. 2017;2017:8194940. http://doi. org/10.1155/2017/8194940. PMid:28243314. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8194940
Singh AG, Singh S, Singh PP. YouTube for information on rheumatoid arthritis--a wakeup call? J Rheumatol. 2012;39(5):899-903. http://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.111114. PMid:22467934. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.111114
Forbes. Brasil é o terceiro país com mais usuários do YouTube em 2023 [Internet]. São Paulo: Forbes Group; 2023 [cited 2023 Sep 5]. Available from: https://forbes.com.br/forbes-tech/2023/05/brasil-e-o-terceiro-pais-com-mais-usuarios-do-youtube-em-2023/#:~:text=n%C3%A3o%20%C3%A9%20baixa.-,De%20 acordo%20com%20o%20banco%20internacional%20de%20 dados%20Statista%2C%20atualmente,no%20primeiro%20 m%C3%AAs%20do%20ano
Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1545-602. http://doi.org/10.1016/ S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMid:27733282.
Kim A, Moravec PL, Dennis AR. Combating fake news on social media with source ratings: the effects of user and expert reputation ratings. J Manage Inf Syst. 2019;36(3):931-68. http://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2019.1628921. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2019.1628921
Garrett R, Poulsen S. Flagging Facebook falsehoods: self identified humor warnings outperform fact checker and peer warnings. J Comput Mediat Commun. 2019;24(5):240-58. http://doi. org/10.1093/jcmc/zmz012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jcmc/zmz012
YouTube. Informações sobre conteúdos relacionados à saúde [Internet]. Mountain View: Google Inc.; 2024 [cited 2024 Feb 15]. Available from: https://support.google.com/youtube/ans wer/9795167?sjid=8543761559199999074-SA