Adult human neural cells in culture following traumatic brain injury
Main Article Content
Abstract
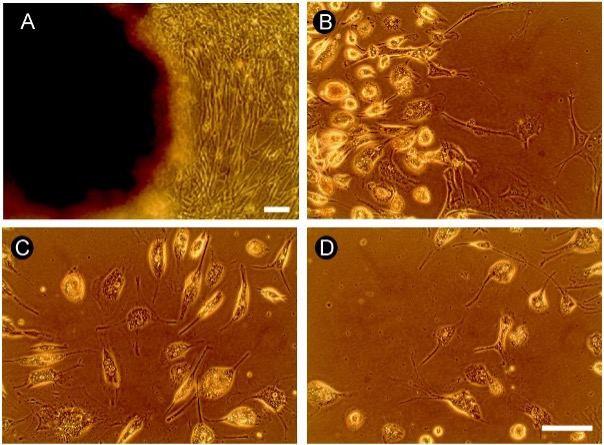
Objective: The present study aims to evaluate the viability of adult human neural cells in culture obtained from traumatized brain tissues collected in emergency surgery procedures. Methods: Exploratory, descriptive, quantitative and cross-sectional study evaluating samples obtained from patients who underwent traumatic brain injury with extrusion of brain tissue submitted to cell culture in a standardized medium, being preserved during 168h. After observation under phase contrast microscopy and immunohistochemical processing for neuronal (MAP-2) and glial (GFAP) markers, morphometric parameters of neural cells (cell body area, dendritic field length and fractal dimension) were evaluated using ImageJ software, with data obtained after 24, 72 and 168h being compared using non-parametric Kruskal Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s post hoc test. Results: The explant of the nervous tissue revealed a consolidated pattern of cell migration into the culture medium. Cell proliferation, upon reaching confluence, presented an aspect of cellular distribution juxtaposed along the culture medium at all time points analyzed. Both neurons and glial cells remained viable after 168h in culture, with their morphologies not varying significantly throughout the time points evaluated. Immunohistochemistry for MAP-2 showed a relatively well-preserved cytoskeletal organization. GFAP immunoreactivity revealed activated astrocytes especially at the later time point. Conclusions: Our results point out the viability of cell culture from traumatized human nervous tissue, opening up perspectives for the use of substances of natural origin that may contribute neuroprotectively to neuronal maintenance in culture, allowing future translational approach.
Article Details
Authors maintain copyright and grant the HSJ the right to first publication. From 2024, the publications wiil be licensed under Attribution 4.0 International 
 , allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
, allowing their sharing, recognizing the authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are authorized to assume additional contracts separately for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the work published in this journal (e.g., publishing in an institutional repository or as a book chapter), with acknowledgment of authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Authors are encouraged to publish and distribute their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their personal page) at any point after the editorial process.
Also, the AUTHOR is informed and consents that the HSJ can incorporate his article into existing or future scientific databases and indexers, under the conditions defined by the latter at all times, which will involve, at least, the possibility that the holders of these databases can perform the following actions on the article.
References
Van Itallie TB. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) in collision sports: Possible mechanisms of transformation into chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Metabolism. 2019;100S:153943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2019.07.007
Graham NSN, Sharp DJ. Understanding neurodegeneration after traumatic brain injury: from mechanisms to clinical trials in dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019;90(11):1221-33. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2017-317557
Sariaslan A, Sharp DJ, D'Onofrio BM, Larsson H, Fazel S. Long-Term outcomes associated with traumatic brain injury in childhood and adolescence: a nationwide Swedish cohort study of a wide range of medical and social outcomes. PLoS Med. 2016;13(8):e1002103. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002103
Dewan MC, Rattani A, Gupta S, Baticulon RE, Hung YA, Punchak M, et al. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2018;130(4):1080-97. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.10.JNS17352
Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1):56-87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30415-0
Ortiz-Prado E, Mascialino G, Paz C, Rodrigue-Lorenzana A, Gómez-Barreno L, Simbaña-Rivera K, et al. A nationwide study of incidence and mortality due to traumatic brain injury in Ecuador (2004-2016). Neuroepidemiology. 2020;54(1):33-44. https://doi.org/10.1159/000502580
Maas AIR. Traumatic brain injury: integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16:987-1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30371-X
Taylor CA, Bell JM, Breiding MJ, Xu L. Traumatic brain injury-related emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths - United States, 2007 and 2013. MMWR Surveillance Summ. 2017;66(9):1-16. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.ss6609a1
Daugherty J, Waltzman D, Sarmiento K, Xu L. Traumatic Brain Injury-Related Deaths by Race/Ethnicity, Sex, Intent, and Mechanism of Injury - United States, 2000-2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68(46):1050-6. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6846a2
Bonow RH, Barber J, Temkin NR, Videtta W, Rondina C, Petroni G, et al. The outcome of severe traumatic brain injury in Latin America. World Neurosurg. 2018;111:e82-e90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.11.171
Almeida CER, Sousa-Filho JL, Dourado JC, Gontijo PAM, Dellaretti MA, Costa BS. Traumatic brain injury epidemiology in Brazil. World Neurosurg. 2016;87:540-547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.10.020
Magalhaes ALG, Barros JLVM, Cardoso MGF, Rocha NP, Faleiro RM, Souza LC, et al. Traumatic brain injury in Brazil: an epidemiological study and systematic review of the literature. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2022;80(4):410-23. https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x-anp-2021-0035
Rosenbaum AM, Gordon WA, Joannou A, Berman BA. Functional outcomes following post-acute rehabilitation for moderate-to-severe traumatic injury. Brain Inj. 2018;32(7):907-14. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2018.1469040
Cariello AN, Perrin PB, Agudelo YR, Plaza SLO, Quijano-Martínez MC, Trujillo MA et al. Predictors of longitudinal depression trajectories after traumatic brain injury in Latin America: A multi-site study. NeuroRehabilitation. 2020;46(2):205-12. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-192972
Scheid R, Walther K, Guthke T, Preul C, von Cramon DY. Cognitive sequelae of diffuse axonal injury. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(3):418-24. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.63.3.418
Shively S, Scher AI, Perl DP, Diaz-Arrastia R. Dementia resulting from traumatic brain injury: what is the pathology? Arch Neurol. 2012;69(10):1245-51. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2011.3747
Cardoso MGF, Faleiro RM, Paula JJ, Kummer A, Caramelli P, Teixeira AL, et al. Cognitive impairment following acute mild traumatic brain injury. Front Neurol. 2019;10:198. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00198
Guimarães JS, Freire MAM, Lima RR, Souza-Rodrigues RD, Costa AMR, dos Santos CD, et al. Mecanismos de degeneración secundaria en el sistema nervioso central durante los trastornos neuronales agudos y el daño en la sustancia blanca. Rev Neurol. 2009;48(6):304-10. https://doi.org/10.33588/rn.4806.2008512
DeKosky ST, Asken BM. Injury cascades in TBI-related neurodegeneration. Brain Inj. 2017;31(9):1177-82. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2017.1312528
Morganti-Kossmann MC, Rancan M, Stahel PF, Kossmann T. Inflammatory response in acute traumatic brain injury: a double-edged sword. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2002;8(2):101-5. https://doi.org/10.1097/00075198-200204000-00002
Freire MAM. Pathophysiology of neurodegeneration following traumatic brain injury. West Indian Med J. 2012;61(7):751-5. https://doi.org/10.7727/wimj.2012.003
Gähwiler BH. Nerve cells in culture: The extraordinary discovery by Ross Granville Harrison. Brain Res Bull. 1999;50:343-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-9230(99)00097-0
Van der Worp HB, Howells DW, Sena ES, Porritt MJ, Rewell S, O'Collins V, et al. Can animal models of disease reliably inform human studies? PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000245. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000245
Gibbons HM, Dragunow M. Adult human brain cell culture for neuroscience research. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42(6):844-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2009.12.002
Ray B, Chopra N, Long JM, Lahiri DK. Human primary mixed brain cultures: preparation, differentiation, characterization and application to neuroscience research. Mol Brain. 2014;7:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-014-0063-0
Hong YJ, Do JT. Neural lineage differentiation from pluripotent stem cells to mimic human brain tissues. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:400. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00400
Spaethling JM, Na YJ, Lee J, Ulyanova AV, Baltuch GH, Bell TJ et al. Primary cell culture of live neurosurgically-resected aged adult human brain cells and single cell transcriptomics. Cell Rep. 2017;18(3):791-803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.066
Park TIH, Schweder P, Lee K, Dieriks BV, Jung Y, Smyh L et al. Isolation and culture of functional adult. Brain Commun. 2020;2(2):fcaa171. https://doi.org/10.1093/braincomms/fcaa171
Lucena EES, Guzen FP, Cavalcanti JRLP, Marinho MJM, Pereira WO, Barboza CAG et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow in the presence of conditioned medium of the facial nerve and fibroblast growth factor-2. ScientificWorld Journal. 2014;2014:457380. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/457380
Freire MAM, Faber J, Picanco-Diniz CW, Franca JG, Pereira A. Morphometric variability of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase neurons in the primary sensory areas of the rat. Neuroscience. 2012;205:140-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.12.029
Capizzi A, Woo J, Verduzco-Gutierrez M. Traumatic Brain Injury: An overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and medical management. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):213-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2019.11.001
McInnes K, Friesen CL, MacKenzie DE, Westwood DA, Boe SG. Mild Traumatic brain injury (mTBI) and chronic cognitive impairment: A scoping review. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0174847. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174847
Estrada-Rojo F, Martínez-Tapia RJ, Estrada-Bernal F, Martínez-Vargas M, Perez-Arredondo A, Flores-Avalos L, et al. Models used in the study of traumatic brain injury. Rev Neurosci. 2018;29(2):139-49. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2017-0028
Wu YH, Rosset S, Lee TR, Dragunow M, Park T, Shim V. In Vitro Models of Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(17):2336-72. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2020.7402
Darmanis S, Sloan SA, Zhang Y, Enge M, Caneda C, Shuer LM, et al. A survey of human brain transcriptome diversity at the single cell level. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(23):7285-90. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1507125112
Zhang Y, Sloan SA, Clarke LE, Caneda C, Plaza CA, Blumenthal PD, et al. Purification and characterization of progenitor and mature human astrocytes reveals transcriptional and functional differences with mouse. Neuron. 2016;89(1):37-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.11.013
Gumy LF, Katrukha EA, Grigoriev I, Jaarsma D, Kapitein LC, Akhmanova A, et al. MAP2 defines a pre-axonal filtering zone to regulate KIF1-versus KIF5-dependent cargo transport in sensory neurons. Neuron. 2017;94(2):347-362.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.03.046
Freire MAM, Rocha GS, Costa IM, Oliveira LC, Guzen FP, Cavalcanti JRLP. Roles of the terpenoid Astragaloside IV in altered states of the nervous system: an updated review. Res Soc Develop. 2022;11(6):e11711628861. https://doi.org/10.33448/rsd-v11i6.28861
Miguel CA, Noya-Riobó MV, Mazzone GL, Villar MJ, Coronel MF. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of resveratrol after experimental nervous system insults. Special focus on the molecular mechanisms involved. Neurochem Int. 2021;150:105188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105188
Fang J, Wang Z, Wang P, Wang M. Extraction, structure and bioactivities of the polysaccharides from Ginkgo biloba: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;162:1897-905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.141